Contents
This page reviews the GDMA product.
| For GDMA installation and upgrade information see the GroundWork knowledge base under [FLEX:GroundWork Distributed Monitoring Agent]. |
Introduction
The GroundWork Monitor Enterprise product family consists of GroundWork Monitor Enterprise Edition (GWMEE), GroundWork Monitor Standby Notification Server, Linux Child Servers, Windows Child Servers, GroundWork Network Management Suite (NMS) add-ons, and GroundWork Distributed Monitoring Agents (GDMAs).
The purpose of this document is to describe the use cases, modes of operation, and application design considerations for GDMAs.
A GDMA consists of memory resident programs that perform monitoring checks on individually configurable time intervals, and reports the results to GWMEE. Configuration files containing program directives, including alarm thresholds and other parameters are periodically downloaded from GWMEE. The agent performs monitoring checks by supplying necessary arguments to small disk resident programs called plugins, and then running them with the supplied options. The plugin set provided for the agent is consistent with the plugins distributed with GWMEE, as well as useful plugins specific to the OS of the monitored server, for example, vbs or powershell plugins for Windows systems.
GDMAs support multiple modes of operation, including installation and configuration, normal operations, and failure modes. Since GDMAs are designed to operate under the control of a GWMEE system, there are corresponding functions and features on the GWMEE system that support each of these operating modes. Each of these modes is discussed in more detail in the section called Description of GDMA Operation below. GDMAs can be employed to monitor the single host on which they are installed (single host mode) or to monitor multiple hosts from a single GDMA installed on a single host which is referred to as the multi-host configuration. Multi-host configuration is used with the Windows GDMA to create the Windows Child server and with any supported operating system to provide economical monitoring on customer premises for the Managed Service Providers (MSPs).
Describing the normal operating mode for a single GDMA monitoring a single monitored server helps to introduce the subject.
GDMA Data and Control Flow
A single Linux GDMA and the GWMEE which controls it is illustrated in the following figure.
Figure: GDMA Data and Control Flow
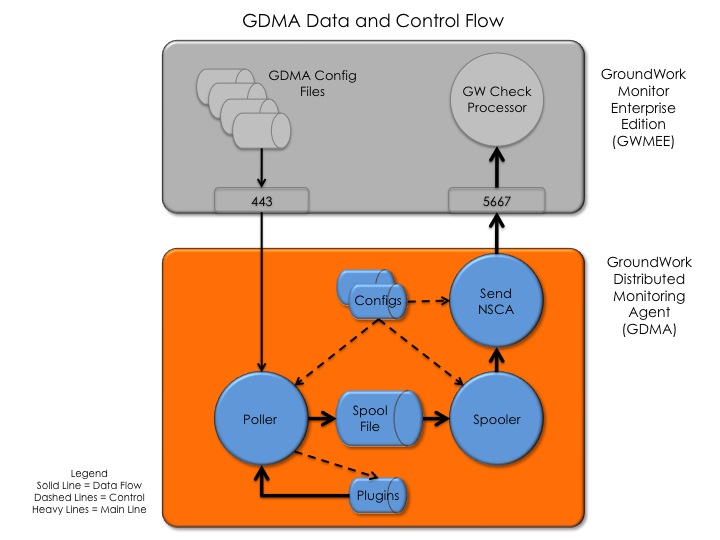
The GDMA consists of two Perl programs; a Poller and a Spooler, the binary program for Send_NSCA, and two or more configuration files. Also included are between 100 and 200 plugins, and a spool file containing monitoring and error messages which are waiting to be transmitted to GWMEE.
In normal operation, the Poller program reads the configuration file, calls the plugin, and supplies the required arguments to configure it to collect the required metric. It then executes the plugin as a "check", and writes the results to the Spool File. The Poller then waits until the scheduled time for the next check and repeats the process. Individual checks can be executed each cycle or on a defined multiple of cycles, giving the administrator individual control over each check's schedule.
At defined intervals the Spooler reads the Spool File, calls the "Send_NSCA" program and transmits one or more of the messages containing monitoring check results to the GWMEE system using the NSCA application protocol. Operation of the Poller, Spooler, and Send NSCA modules are controlled by parameters contained within the GDMA configuration files (see detailed configuration file specifications and list of directives in Reference 1).
| The default port for NSCA communication is 5667, however, it can be reconfigured to a different port number on both sides of the interface if required. |
The configuration file contains a number of error handling and control parameters which are used by the Poller and the Spooler to help ensure the reliable operation of the GDMA, including a subroutine that verifies the validity of the configuration file itself. Error messages are normally written to the Spool file for transmission to the GWMEE system where they can be reviewed and analyzed by system operators using the Event Console application.
Monitoring results reported to GWMEE are presented as service check results. Host health checks can be performed actively from GWMEE if access to the monitored server is permitted. If active access is not permitted, an algorithm is used by the GWMEE to distinguish between service alarm and host failure. Active checks of host health are preferred where permitted for performance reasons.
Routine maintenance of the GDMA configuration is performed by editing the externals text files within the Monarch subsystem on GWMEE. Either automatically or as an operator action, the Configuration application updates the externals config files in the appropriate directory for retrieval.
At regular intervals defined in the config files the Poller initiates an HTTP or HTTP(S) connection and looks up the time stamp of the config file stored on GWMEE. If the file on GWMEE is more recent that the config file on the GDMA, the Poller fetches the GDMA configuration file from GWMEE and replaces the older file on the GDMA with the most recently updated file.
About Automated Agent Registration
The combined GWMEE 6.7.0 and GDMA 2.3.0 releases contain support for a new GDMA client auto-registration capability. This facility is designed to allow hosts monitored via GDMA to be automatically added to the central server, with very little effort by the administrator.
Automated Agent Registration was implemented to reduce the administrator's burden when adding many GDMA-monitored hosts to the monitored infrastructure. Many of the simple tasks are highly automated, allowing the administrator to concentrate more on exceptions and the overall monitoring design.
When Automated Agent Registration is active, each new GDMA client makes an auto-registration request to connect to the GroundWork Monitor server and receive its marching orders. The server validates the request, corrects the submitted host attributes if necessary, adds the host to the configuration if it is not already there, builds an externals file containing the details of the monitoring checks the client should run, and finally returns the validated hostname (or error messages) to the client. Refer to Automated Agent Registration in this section of the Bookshelf for additional information.
Use Cases and Application Notes
GDMAs are intended to be used for the following use cases:
Cost Effective and Reliable Monitoring Capacity Enhancement
GWMEE can be configured to collect monitoring information by active polling or to receive monitoring information passively from external sources. The number of hosts that can be monitored passively is generally an order of magnitude greater than the number that can be monitored by active polling. GDMAs submit monitoring results to the GWMEE system passively, and thus enable significantly larger scale monitoring systems than those based exclusively on active polling.
GDMA incorporates automation features to enable distribution and configuration of large numbers of agents with relative ease. Auto registration and auto configuration are described in detail in Reference 1.
In monitoring applications where passive checks can displace active polling in whole or in part, the number of servers performing active polling is substantially reduced or eliminated. This reduces or eliminates the need for redundant polling servers and maximizes overall system reliability by reducing complexity. The cost per monitored node will generally be lower in installations in which most data collection is performed with GDMAs.
| Design Engineering Note Design Engineering Notes are written in italics to provide informal and non-binding guidance that may be useful to customers and partners who are designing monitoring solutions for end user organizations. Going forward, GroundWork is likely to encourage all of it's customers to make use of GDMAs for all server monitoring regardless of the number of devices. This change will be enabled by slowly converting existing profiles based on SSH and NRPE to GDMA. The reasons for this are the following:
|
Internal Security Zoning
Network security policies often prohibit communication needed to employ active polling methods for certain security zones. Some of the specific examples where this requirement is encountered are the following:
- A DMZ
- Domains containing servers managing clinical trials information
- Domains containing database servers when the GWMEE server cannot be placed in the database server zone.
- A customer premise for a Managed Service Provider (MSP) which is separated from the MSP by the customer's firewall.
The ability of the GDMA/GWMEE combination to be configured so that all necessary communications are initiated from the GDMA supports the use of GDMA in all security zones separated by firewall policies from the GWMEE system.
| Application Engineering Note
This use case requires GDMA to be deployed in environments where bi-directional communication between GWMEE and the monitored server is not possible. In these environments standard "Host Alive" check methods are replaced with algorithmic checks of available service state information for each host. Contact GroundWork Support for more information on the required host check. |
Agentless Windows Server Monitoring
The multi-host configuration of the Windows GDMA can be configured to perform active polling for Windows Servers within the same Active Directory domain. This configuration uses plugs that run powershell and vb script, and access Perfmon and WMI information on the monitored Windows servers. This avoids installation of individual agents on the monitored Windows servers, with the exception of the system on which the Windows multi-host GDMA is installed.
Cloud Computing Environments
The unique requirements for monitoring in private and public cloud environments create additional requirements for distributed agents:
- The use of GDMA distributes most of the workload for the monitoring function onto the servers that are being monitored, which means that monitoring capacity is much more self-contained and linear with regard to the number of cloud-based servers being monitored. This makes the monitoring system itself much more scalable and flexible without the need to plan for additional polling capacity.
- When additional monitored servers are added to the cloud, the GroundWork Monitor server can query the cloud Application Programming Interface (API) to determine which image has been loaded on the virtual device. The corresponding monitoring profile can be selected and assigned. The use of GDMA simplifies this use case, since the configuration file can be automatically generated and made available to the GDMA poller on its next request for an update. This process is logged, and can trigger instantiation of the updated configuration as needed.
Definitions and Abbreviations
The following definitions and abbreviations of commonly used terms are provided for standardization and reference.
- "GroundWork Monitor Enterprise Edition or GWMEE" is the standard GroundWork enterprise monitoring product which hosts the monitoring configurations, and collects and presents the resulting availability and performance information. GWMEE refers to the top level GroundWork monitoring system, including the hardware that it runs on. The word "server" or "system" would normally not be added either to the name or the abbreviation GWMEE. In a system containing GroundWork Child Servers, it is understood that GWMEE includes the term "parent server".
- "GroundWork Standby Notification server" or "Standby server" is a special configuration of the GWMEE product software which provides continuity of notifications in the event that GWMEE becomes unavailable. This term is not normally abbreviated, so for convenience this product may be referred to as "Standby server" provided that this usage occurs in the document after this definition or after first use of the complete term. The Standby server monitors the GWMEE as a hot standby which is to say that it receives and processes all of the monitoring information received or processed by GWMEE, except that its notification process is continually reset to disabled by a process that verifies that the GWMEE is functioning. Thus at any time that GWMEE becomes unavailable, notifications are immediately begun by the Standby server. Standby Server is designed to provide continuity for notifications of outages during the period of time required to restore the GWMEE to service. It is not a High Availability system nor is it designed to take over the monitoring configuration control functions of GWMEE during a GWMEE outage. For information about High Availability options for GWMEE, please contact GroundWork Sales.
- GroundWork Linux Child server or simply "Linux Child", is a special configuration of the GWMEE software which provides added capacity for performing active monitoring checks. In typical installations, one or more Linux Child servers receive configuration updates from the GroundWork Monitor server and report monitoring results to the GWMEE server and also to a Standby Notification server if one is installed. Traps, logs, and GDMA monitoring results are not normally directed to Linux Child servers and database updates, user interfaces, and notifications are not normally enabled on Linux Child servers.
- GroundWork Distributed Monitoring Agent consists of memory resident programs installed on servers to be monitored that perform monitoring checks on individually configurable time intervals and report the results to a GWMEE system.
- GroundWork Windows Child server is a special multi-host configuration of the Windows GroundWork Distributed Monitoring Agent (GDMA) which provides added capacity for performing active monitoring checks of multiple Windows servers. In typical installations, one or more Windows Child servers receive configuration updates from the GWMEE server and report monitoring results to the GWMEE server and also to a Standby Notification server if one is installed.
- GroundWork Network Management Suite (NMS) is a combination of several open source modules which may be optionally added to GWMEE to extend the functionality of GroundWork for network monitoring and management. The GroundWork NMS can be co-hosted on the same server as the GWMEE or distributed to one or more servers dedicated to this use.
- "Monitored" Host is a server, router, switch, load balancer, fire wall, storage device, or application which is being monitored for availability and performance by a GWMEE system. This is distinguished from a "monitoring" host which is a GWMEE, Standby server, child server, or GNMS server.
- Plugins are programs, normally invoked at the command line or by an agent like GDMA, which collect monitoring information such as CPU, Swap, or disk utilization, lists of running processes, table space extents, etc., and return the results in a defined format. The results include whether the test exceeds either a warning or critical threshold value associated with the particular check, as well as any performance data collected, thus plugins return both state and metrics.
- A managed service provider (MSP) provides delivery and management of network-based services, applications, and equipment to enterprises, residences, or other service providers. MSPs serve as outsourcing agents for companies looking to reduce IT operations costs.
- "Target System" is the title of one of the configuration directives in the GDMA which refers to the names or IP addresses to which the spooler is to transmit the spool file contents. We will not use this term in standard GroundWork product documentation to avoid confusion with common informal usage which refers to the system being monitored as a target system. Instead we will refer to the system to which results are sent from a GDMA as the GWMEE and the Standby Notification server.
Description of GDMA Modes of Operation
GDMAs have been designed with modes of operation for installation, auto configuration, configuration maintenance, normal operation, and continued operation in failure modes. The following provides an overview of the major options available for each of these operating modes for the product.
Installation Mode
GDMAs can be installed on the target server on which they are to run in several different ways, depending on plant conditions, life cycle point, and other circumstances.
- One installation mode is to simply install the GDMA environment as part of a server installation image. Thus each time the server operating system and applications are installed, the GDMA and its attendant files are installed along with it. The installer would normally be configured for unattended operation in this case.
- A second possible installation method is to package the GDMAs as required by the customer's software configuration management and patch distribution system. The GDMA is packaged in a binary installer, which is easily wrapped using a number of possible software distribution utilities (Puppet, OCS, cfengine, Altiris, etc). The installer would normally be configured for unattended operation in this case.
- A third GDMA installation mode is to simply log in to the monitored host and download the GDMA installer specific to the server's operating system from the GWMEE system and proceed as with any other GroundWork software installation using the standard product installer. This process can be configured for either attended or unattended operation.
Regardless of the specific method, the Linux GDMA and its attendant files will be installed in a usr/local/groundwork directory that is created by the GDMA installer. Solaris and AIX will use /opt/groundwork, and the Windows GDMA will be installed in a directory determined by the Windows distribution and architecture. In english versions of 32-bit MS windows, this is "C:\Program Files", and in 64-bit MS Windows, it is "C:\Program Files (x86)". This default may be different in different language distributions of Windows, and in the Windows case may be over-ridden by a user-supplied directory at install time.
| Linux, Solaris, and AIX versions of the GDMA cannot be installed in user-supplied directories. |
Auto Configuration Mode
Initial configuration of the GDMA will normally be performed using the auto configuration mode. Multi-host configurations, including Windows Child Server configurations, cannot use this mode.
Autoconfiguration mode is recommended for the creation of initial configurations for all GDMA installations with a single agent monitoring a single host. For this mode the GDMA is initially deployed with a special auto configuration file instead of a standard configuration file. The following figure illustrates the data flow for autoconfiguration on both the GDMA and GWMEE.
Figure: Auto Configuration Process Flow
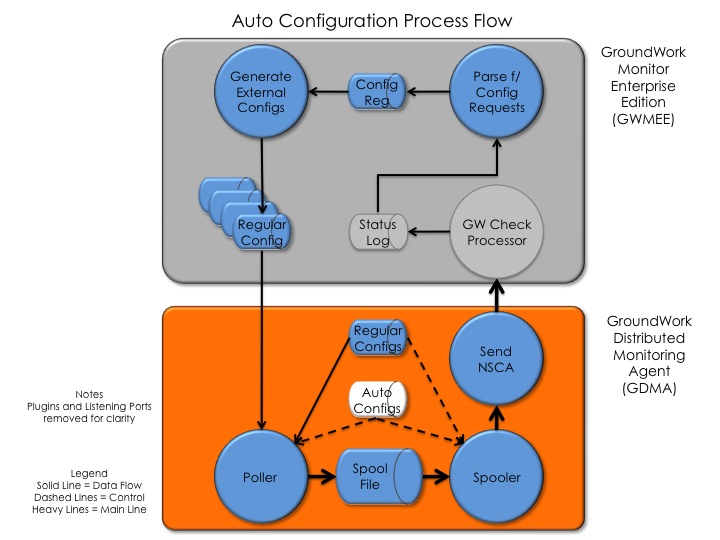
Upon initialization of the Poller, the GDMA reads basic configuration directives from the auto configuration file, and then attempts to use these to find a normal configuration file. If this file is not present, and cannot be obtained, it continues in auto-mode.
Based on the auto config directives, the Poller determines the host name and the OS of the system it has been installed on and writes an auto registration message in the format of a standard service check result to the Spool file. The Spooler reads the message and under the control of directives contained in the auto config file communicates the message to the GWMEE system as a result for a special automation host.
The delivery address of the GWMEE server in the auto config file is normally given as a name, rather than an address, so that DNS or an equivalent naming service is relied upon to provide the address. To use this feature, the administrator must create the corresponding naming service entry for the GWMEE prior to first use of the auto configuration mode by GDMAs. The default name is gdma-autohost, though this is configurable at installation time. Alternatively, the administrator can place the IP address of the GWMEE in the auto config file at install.
In this way the Poller's auto registration message is delivered by the Send_NSCA program to GWMEE as shown above. The arriving message from the GDMA is delivered to a monitoring service for a host named "gdma-autohost." All such messages from GDMAs are delivered to the same host-service and written, like all other service check results to the Nagios Log.
| There are normally no thresholds associated with this service and thus no alarms will result from this process. |
Periodically, as scheduled by cron, a program reads the Nagios Status Log and writes all of the autoregistration messages to a separate Configuration Request Log file. A second program scheduled by cron reads this file, and generates the regular configuration files (externals) that are appropriate to the operating system of the monitored host containing the GDMA. It also adds the GDMA hosts to the Monarch configuration database and associates the hosts with standard profiles based on the operating systems reported in the request configuration message. The generated configuration files are placed into the distribution directory on GWMEE corresponding to the file path name which was placed in the GDMA auto configuration file. This permits the Poller to download its regular configuration file.
| GDMA Configuration files are also referred to as External files. |
When the Poller cycle begins again, it downloads the regular configuration file, and uses it as the source of all program directives. The auto-configuration file is still read first, and defaults not overwritten in the regular configuration file are used. Thus, the monitoring checks called for in the regular configuration file begin to be made and written to the spool file for communication to GWMEE.
The final step in the autoconfiguration process is to run a Commit from the Configuration system which instantiates the self registered hosts to the GroundWork Nagios instance, the GroundWork Foundation databases, and thence to the user interface and notification processes. When this is complete the new self-registered hosts will be properly reflected in the user interface. When service freshness and host health checks are properly configured as per the documentation, the new hosts will be in full monitoring operation. The choice of host check used depends upon whether the GWMEE system can access the monitored host with ICMP, based upon existing security policies as discussed previously.
The following steps must be taken to enable the auto-configuration mode prior to GDMA deployment (see the GDMA Quick Start reference in the Bookshelf)
- GWMEE Server Address and Name must be added to DNS or other naming service (or the address specified to the GDMA at installation time.)
- Auto configuration host and service and its standard profile configured on GWMEE using the Configuration interface.
- Externals Enabled on the Configuration Control menu.
- GroundWork Configuration Groups corresponding to Windows and Non-Windows GDMA need to be configured in order to permit externals configuration files to be generated upon request.
- GDMA-releated profiles must be loaded, or equivalent profiles created and referenced in the auto-config scripts.
| Application Notes Clearly, auto configuration is a powerful technique that many GroundWork users will make use of for getting started with GDMA. There are some use cases involving embedded systems, the configuration of multi-host mode, etc. where it may be useful to pre-configure a complete configuration file prior to deploying the agent, and thus avoid the use of auto configuration. GroundWork professional services are available for consultation on such special cases. If the GroundWork/GDMA administrator doesn't have immediate access to make changes on DNS or other naming service, the GWMEE server address can be specified to the GDMA at install time, so that the spooler can properly communicate with the GroundWork system. The Bookshelf product documentation contains procedural guidance on the installation and initial configuration of GDMAs and the GWMEE systems which control them. After the initial configuration of the GDMA, more complex monitoring profiles can be added by creating new external configuration files for additional services. |
Configuration Maintenance Mode
After initial configuration is completed with auto configuration, the GroundWork Administrator uses Configuration as usual, to update thresholds, add and delete service checks, assign and change host group assignments, etc. Optionally, each time a Commit is performed, the externals files will be renewed and made available to the GDMA poller when it requests them. No specific consideration must be made for the fact that the checks are being made by GDMA as opposed to any other method, except that text content of the externals files must be edited to affect configuration changes on GDMA monitored hosts and services, rather than using the nominal configuration screens.
Agent and plugin updates currently require that the agent be uninstalled using the script that is supplied and installed with the agent and the new version of the agent installed using one of the available installation modes.
| Application Engineering Notes The plugins that are loaded onto the monitored system are a superset of the plugins needed to implement any particular coverage profile. Thus the addition of plugins is not frequently required after the initial load except for new plugins that may be written by GroundWork customers. The GWMEE can host a set of plugins for download by architecture, allowing maintenance of existing plugins, and the addition of user-supplied plugins to multiple GDMAs. |
Normal Operation Mode
Normal operation of GDMAs is described in the first section of this document. To supplement that description, the following additions are made:
The GDMA can be configured to send its spool file contents to more than one GWMEE system. The most common example is a GWMEE and a Standby Server.
When a GDMA is installed as a Windows Child server or a multi-host GDMA, the monitoring results are delivered to GWMEE addressed for the correct host/service. In this configuration, there will be a regular configuration file installed on the GDMA corresponding to each of the hosts that the GDMA is monitoring. Installation and configuration of Windows Child server is provided via a professional services engagement.
Failure Modes
GDMAs are designed to be fault tolerant in the face of the following assumed modes of failure:
- Corruption of a configuration file. The GDMA enters auto config mode when the regular configuration file is found to be corrupt. If the configuration file is present and is valid, but the new configuration file is not available due to a connection failure or it's having been removed or restricted on GWMEE, it keeps on executing in normal mode with the previously read valid configuration for a configurable period (default is 3 days).
- Plugin execution error. This failure is reported in the service check result as an unknown condition, indicating configuration error.
- Plugin time out is reported in the service check result as defined by the plugin, typically a critical condition.
- Temporary loss of connectivity to the GWMEE is dealt with by spooling results on the monitored host. The default spooling period is 15 minutes, and can be adjusted.
- Troubleshooting modes are supported through the use of command-line switches on the GDMA programs, as well as optional logging levels.
- A crash or halt of any of the GDMA programs will be detected through host freshness checks running on the GWMEE system.
